At this point, we’ve said it a thousand times: Interoperability is foundational for solving healthcare’s biggest problems. At its core, interoperability is simply meaningful communication—moving relevant information from one point to another and ingesting it in a way that’s easily used by the receiver of that information. However, this meaningful communication means profoundly more to the healthcare ecosystem. To understand how interoperability is transforming healthcare delivery, we can look at four key personas: the patient, the provider, the healthcare business, and the healthcare system at large.
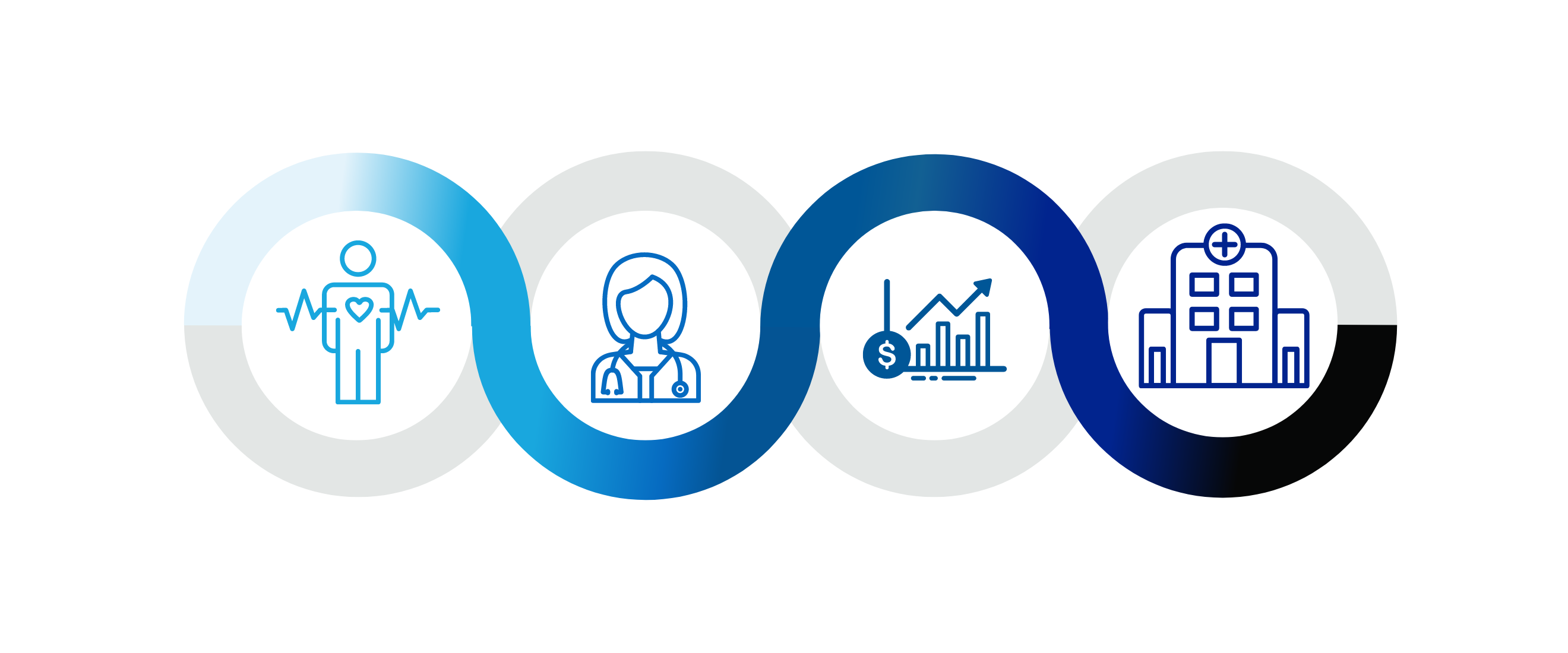
1. The Patient Perspective
For patients, interoperability ensures that the right information is available at the right time, in the right place, and in the right format, within the workflow of their provider. This creates a safer and more efficient care environment. Having an accurate list of allergies, medications, and additional past information is crucial for safe care. Interoperability enhances care coordination and improves the patient experience, as patients are known to their providers before they even arrive.
- Enhanced Safety: Accurate allergy and medication lists reduce the risk of adverse drug reactions and other medical errors.
- Improved Care Coordination: Seamless information flow ensures that all healthcare providers involved in a patient’s care are on the same page, reducing the chances of miscommunication and fragmented care.
- Personalized Care: Providers have access to comprehensive patient histories, enabling more tailored and effective treatment plans.
- Reduced Administrative Burden: Patients no longer need to repeatedly fill out forms or recount their medical history, saving time and reducing frustration.
- Better Health Outcomes: With complete and accurate information, providers can make more informed decisions, leading to improved health outcomes for patients.
Imagine a scenario where a patient with a complex medical history visits a new specialist. Without interoperability, the specialist might not have access to the patient’s full medical records, leading to redundant tests and potentially dangerous gaps in information. With interoperability, the specialist can quickly access the patient’s complete medical history, ensuring more accurate diagnoses and better treatment plans. This seamless flow of information allows providers to focus more on addressing the patient’s concerns rather than gathering and verifying information.
2. The Provider Perspective
For healthcare providers, interoperability streamlines workflows and enhances the quality of care. No longer do providers need to sift through disparate data sources to find relevant information. With timely access to comprehensive patient data, providers can make better and more accurate medical decisions. This efficiency extends beyond the individual patient visit, allowing providers to manage their caseloads more effectively and dedicate more time to patient care.
- Streamlined Workflows: Providers receive all necessary information in a single, consolidated format, reducing the time spent on administrative tasks.
- Enhanced Decision-Making: Access to comprehensive and up-to-date patient information allows providers to make more accurate and timely medical decisions.
- Improved Patient Engagement: With more time to focus on patient care rather than administrative tasks, providers can build stronger relationships with their patients.
- Reduced Burnout: By alleviating the administrative burden, interoperability helps reduce provider burnout and improve job satisfaction.
- Efficient Caseload Management: Providers can manage their patient load more effectively, ensuring that each patient receives the attention they need.
Consider the daily routine of a primary care physician. Each day, they see numerous patients, each with unique medical needs and histories. Interoperability ensures that all necessary information is readily available, from lab results to previous treatments and ongoing medications. This reduces the administrative burden on providers and minimizes the risk of errors. Ultimately, it enables providers to deliver higher-quality care in less time, benefiting both patients and the healthcare system.
3. The Healthcare Business Perspective
Interoperability is equally important for the operational aspects of healthcare businesses. Many workflows in healthcare, such as referral intake and transitions of care, are still manual and inefficient. By digitizing these processes and ensuring seamless information exchange, healthcare businesses can significantly improve their efficiency and effectiveness.
- Automated Workflows: Digitization of manual processes reduces the need for time-consuming and error-prone manual data entry.
- Resource Optimization: Improved efficiency allows healthcare businesses to allocate resources more effectively, doing more with the same or even fewer resources.
- Cost Savings: Streamlined operations and reduced administrative burdens translate into cost savings for healthcare organizations.
- Enhanced Data Accuracy: Automated data exchange reduces the risk of errors associated with manual data entry and improves the accuracy of patient information.
- Improved Coordination: Seamless information exchange facilitates better coordination between different departments and providers, enhancing overall care quality.
Take the example of a hospital’s administrative staff managing patient referrals. In a non-interoperable system, staff might spend hours manually entering data, verifying information, and coordinating with other healthcare providers. This not only consumes valuable resources but also increases the risk of errors and delays. With interoperability, these tasks can be automated and streamlined, allowing staff to focus on higher-value activities. This efficiency translates into cost savings and better resource allocation, enabling healthcare businesses to do more with the same or even fewer resources.
4. The Healthcare System Perspective
One of the biggest challenges in the healthcare system is the cost of care. A significant portion of healthcare costs in the United States, estimated at around 33%, is attributed to unnecessary or low-value care. This often results from a lack of information, leading to duplicated tests and services. Interoperability addresses this issue by providing the necessary information to reduce duplication, eliminate waste, and lower overall healthcare costs.
- Reduced Duplication of Services: Comprehensive patient data reduces the need for redundant tests and procedures, lowering overall healthcare costs.
- Elimination of Waste: Efficient information exchange minimizes administrative waste and enhances operational efficiency.
- Improved Resource Allocation: Better information flow allows healthcare systems to allocate resources more effectively, ensuring that patients receive the right care at the right time.
- Enhanced Patient Safety: Reduced duplication of tests and procedures minimizes patient exposure to unnecessary risks and improves overall safety.
- Lower Healthcare Costs: By addressing inefficiencies and eliminating waste, interoperability contributes to a more cost-effective healthcare system.
For instance, a patient who visits multiple specialists for a chronic condition might undergo the same diagnostic tests multiple times because each provider lacks access to the patient’s complete medical history. Interoperability ensures that all providers can access and share test results, reducing the need for redundant testing. This not only lowers costs but also minimizes the patient’s exposure to unnecessary procedures and associated risks.
Real-World Examples of Interoperability in Action
To illustrate the transformative power of interoperability, consider these real-world examples:
- Health Information Exchanges (HIEs): HIEs facilitate the electronic sharing of health-related information among different healthcare organizations. By connecting disparate systems, HIEs ensure that patient data flows seamlessly between providers, improving care coordination and patient outcomes.
- Electronic Health Records (EHRs): Modern EHR systems are designed to be interoperable, allowing healthcare providers to share patient information securely and efficiently. This interoperability enables providers to access comprehensive patient data, reducing errors and enhancing the quality of care.
- Telehealth and Remote Monitoring: Interoperable systems are crucial for the success of telehealth and remote monitoring. By integrating data from various sources, such as wearable devices and home health monitors, providers can deliver more personalized and timely care to patients, regardless of their location.
Overcoming Challenges to Achieve Interoperability
While the benefits of interoperability are clear, achieving it is not without challenges. These challenges include technical barriers, such as incompatible data formats and legacy systems, as well as regulatory and privacy concerns. However, ongoing efforts to standardize health data formats and implement robust privacy safeguards are paving the way for greater interoperability.
One promising development is the adoption of standards like Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources (FHIR), which provide a framework for exchanging health information electronically. FHIR allows different systems to communicate and share data more effectively, promoting interoperability across the healthcare ecosystem.
The Future of Interoperability in Healthcare
Looking ahead, the future of healthcare will be increasingly data-driven and interconnected. Interoperability will play a central role in this transformation, enabling more personalized and efficient care. Emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) will further enhance the capabilities of interoperable systems, allowing providers to analyze vast amounts of data and generate actionable insights.
For example, AI-powered analytics can identify patterns and trends in patient data, helping providers predict and prevent potential health issues. ML algorithms can assist in clinical decision-making, providing evidence-based recommendations tailored to each patient’s unique needs. These advancements will not only improve patient outcomes but also drive greater efficiency and cost-effectiveness in the healthcare system.
Interoperability is Already Transforming Healthcare
Interoperability is a cornerstone of modern healthcare delivery. By enabling meaningful communication and seamless information exchange, it transforms the patient experience, enhances provider workflows, optimizes healthcare business operations, and reduces overall healthcare costs. As the healthcare industry continues to evolve, interoperability will remain a key driver of innovation and improvement, ultimately leading to a more efficient, effective, and patient-centered healthcare system.